Introduction
Password security is eroding. A bleak image of our dependence on conventional authentication techniques is painted by data breaches, phishing scams, and compromised passwords. With the advent of hyperconnected gadgets and remote labor, a new security paradigm known as “Zero Trust” is taking shape. Under this idea, there is no inherent trust within or outside of a network, and verification is done continuously. Here comes biometrics: the study of identifying people by their distinct biological traits.
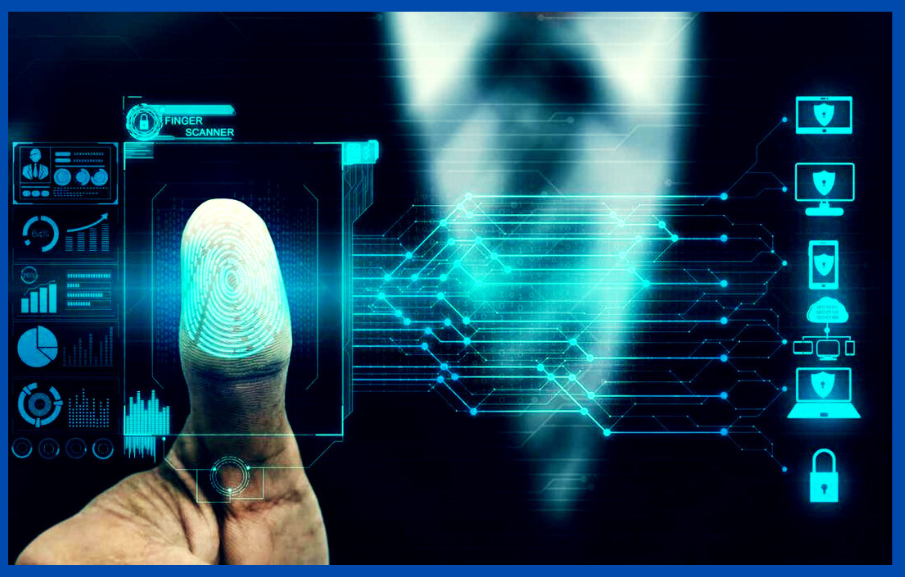

The digital world of today has made biometric data both a target and a shield. Although biometric authentication presents unmatched security benefits, worries about new attacks and privacy violations are significant. These worries have grown as deepfake technology has proliferated, with hackers taking advantage of holes in biometric systems to obtain private data without authorization.
Senior leaders are directly targeted by the evolving cyber threat landscape. Sophisticated biometric and deepfake attacks target C-level executives, with one in three CEOs falling prey to phishing scams. There has never been a more pressing need to strengthen security measures, which has increased demand for creative solutions that can handle the challenges of a zero-trust environment.
Body of Biometrics
Biometrics, from fingerprints to iris scans and beyond, offer an inherent advantage: they can’t be easily shared or replicated. Unlike passwords, your iris pattern or gait is truly yours. This makes them ideal for Zero Trust environments, adding a powerful layer of continuous authentication. Imagine unlocking your corporate network with a blink, accessing sensitive data with a voice command, or seamlessly verifying your identity across devices without ever touching a password field.
Key Features of Biometrics
User-Centric Authentication: Badge empowers users to authenticate seamlessly across multiple devices without compromising privacy or security.
Privacy-Preserving Technology: By eschewing the storage of user secrets or personally identifiable information, Badge mitigates the risk of data breaches and enhances least privilege access.
Quantum-Resistant Security: Future-proofing against emerging threats, Badge operates on a crypto graphically zero-knowledge basis, ensuring robust protection in the face of evolving cyber challenges.
Pros & Cons of Biometrics
Pros:
- Increased Security: Less chance of data breaches and illegal access.
- Privacy-focused: Biometric information is safe to preserve and can be made anonymous.
- Accessibility: Those with impairments who have trouble remembering passwords can use it.
- Convenience and Efficiency: quicker login and a more simplified user interface.
Cons:
- Potential for misuse: Concerns around data privacy and government surveillance.
- Technical challenges: Accuracy and reliability of biometric sensors.
- Cost and infrastructure: Initial investment required for implementation.
- Public perception: Overcoming potential privacy concerns and user adoption.
How to Use Biometrics
Badge’s technology is easily integrated into current Identity and Access Management (IAM) frameworks, and it works flawlessly in a variety of sectors. Organizations may strengthen their security posture against emerging threats and expedite authentication procedures by just requiring one enrolment and authentication on any device.
Biometrics are already finding applications in various fields:
- Financial services: Secure mobile banking and payments.
- Healthcare: Patient identification and medication access control.
- Government: Border security and travel document verification.
- Cybersecurity: Multi-factor authentication for enterprise networks.
- Consumer electronics: Secure device unlocking and personalized experiences.
Call to Action
As threats to digital identity proliferate, the imperative for robust biometric security solutions has never been clearer. Embrace the future of authentication with Badge Inc., and safeguard your organization against the perils of cyber intrusion.
Conclusion
In the quest for a zero-trust world, the role of biometric authentication cannot be overstated. By entrusting individuals with the keys to their digital identity, companies like Badge are forging a path towards enhanced security and privacy in an interconnected landscape. As we navigate the complexities of cyber warfare, let us embrace innovation and resilience to safeguard the integrity of our digital identities.
FAQs
1. What is biometric authentication, and how does it differ from traditional methods?
Using distinctive biological characteristics like fingerprints, iris patterns, or facial features, biometric authentication confirms an individual’s identification. Biometrics, in contrast to more conventional techniques like passwords, are intrinsically linked to specific people and are difficult to counterfeit.
2. What are the advantages of biometric authentication in a zero trust environment?
Biometric authentication adds a layer of continuous verification in a zero trust environment, enhancing security by ensuring that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data or networks.
3. How does deepfake technology impact the security of biometric authentication?
Because deepfake technology enables attackers to construct realistic impersonations through the manipulation of audio or video, it poses a serious danger to biometric authentication systems. Unauthorized access and privacy violations may result from this.
4. Why are senior executives targeted by biometric and deepfake attacks?
Senior executives possess influence within firms and access to sensitive information, making them easy targets for biometric and deepfake attacks. Attackers take advantage of these weaknesses to obtain illegal access and execute intricate schemes.
5. What makes Badge’s biometric authentication technology unique?
Badge’s technology offers user-centric authentication, privacy-preserving features, and quantum-resistant security, making it a robust solution for organizations seeking to strengthen their security posture in a zero trust world.
6. What are the potential drawbacks of biometric authentication?
Concerns around potential misuse, technical challenges related to sensor accuracy and reliability, initial investment costs, and public perception regarding privacy are some of the potential drawbacks of biometric authentication.
7. How can organizations integrate biometric authentication into their existing systems?
Organizations can fortify their security posture against new threats and expedite authentication operations by incorporating Badge’s technology with ease into their existing Identity and Access Management (IAM) frameworks.
8. In which industries are biometrics already finding applications?
Numerous sectors, including consumer electronics, cybersecurity, healthcare, and finance, are already using biometrics for things like safe banking, patient identification, border security, and device unlocking.
9. What are the privacy implications of using biometric authentication?
Although biometric authentication improves security, worries about data privacy and government monitoring persist. Privacy must be given top priority in organizations, and biometric data must be anonymised and securely maintained.
10. How can organizations take action to enhance their biometric security measures?
Employers can take proactive measures by using cutting-edge biometric authentication systems like Badge, teaching staff members the value of security procedures, and keeping up with the latest developments in cybersecurity threats.